Track all of your key business metrics from one screen
GET STARTED
 Facebook Ads
CPM
Facebook Ads
CPM CPM (Cost Per Thousand Impressions) is the cost that an advertiser pays per thousand ad impressions on a social media platform such as Facebook. It is an important metric that helps to measure the effectiveness of ad campaigns and their reach.
With Databox you can track all your metrics from various data sources in one place.
Cost per Mille (CPM), also known as Cost per Thousand, is an advertising metric that represents the average cost an advertiser pays for every one thousand impressions (views) of their ad. It’s typically used to measure the cost-effectiveness of an ad campaign.
CPM is often used in comparison with other advertising metrics, such as CPC (Cost per Click) or CPA (Cost per Action), because it helps advertisers get more granular insight into the efficiency of different advertising campaigns, channels, or platforms.
Cost per Mille (CPM) is calculated by dividing the total cost of an advertising campaign by the number of impressions and then multiplying by 1,000.
Here’s the exact formula:
CPM = (Total Cost / Total Impressions) * 1000
For example, if an advertiser spends $500 for 50,000 impressions, the CPM would be
CPM = ($500 / 50,000) * 1000 = $10
This means that the advertiser is paying $10 for every one thousand impressions.
No matter which platform you run ads on, CPM will be one of the main metrics you should keep an eye on.
To help you better assess your campaign’s performance, we pulled out some benchmark data from our product that you might find useful.
Keep in mind that these numbers also highly depend on your specific industry and campaign type.
If you want to stay on top of future trends and be able to instantly compare your performance to companies just like yours (in any given industry), you can join our Benchmark Groups – it’s free for everyone!
Because the CPM rate is influenced by a variety of different factors, many marketers struggle to improve it.
But after talking to hundreds of experts and conducting dozens of reports on the topic, we’ve narrowed down some of the main tactics they use to improve their CPM:
More resources to help you improve:
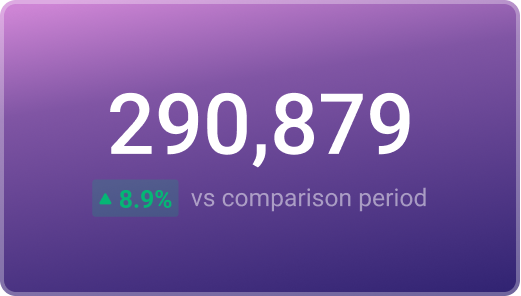
Used to show a simple Metric or to draw attention to one key number.
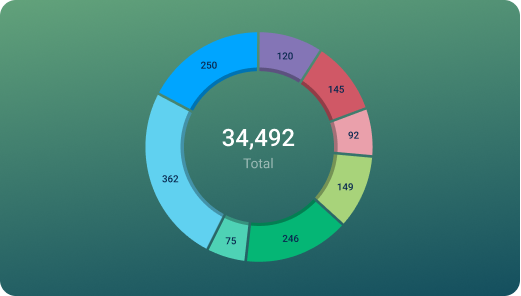
Used to illustrate numerical proportions through the size of the slices.
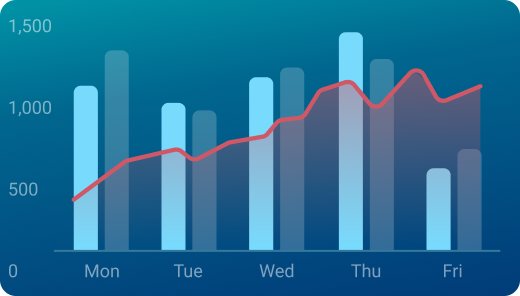
Used to show comparisons between values.
Databox is a business analytics software that allows you to track and visualize your most important metrics from any data source in one centralized platform.
To track CPM using Databox, follow these steps:
 Goals
Goals Scorecards
Scorecards Metric Digest
Metric Digest Metric Builder
Metric Builder Data Calculations
Data Calculations Performance Screen
Performance ScreenThis dashboard helps you inspect every step of your e-commerce funnel so that you can quickly address problem areas.




Use this Facebook Ads advanced report to share high-level and in-depth metrics of your Facebook Ads performance. Present an overview of key metrics like Impressions, CPC, Cost per Lead, ROAS, and more.

CPM, CPC, and CPA are all popular advertising metrics that are used for measuring different aspects of campaign performance.
Each metric serves a different purpose and is used to evaluate different aspects of an advertising campaign.
There are several factors that determine your campaign’s CPM rate, including:
It’s important to note that these factors can interact with each other and CPM rates can vary significantly based on their combinations.
Spotting anomalies in your CPM rate shouldn’t be an immediate reason to panic, but it’s important that you follow it up with a granular investigation and get to the root of the problem.
Here are some of the first things you should assess:
