Track all of your key business metrics from one screen
GET STARTED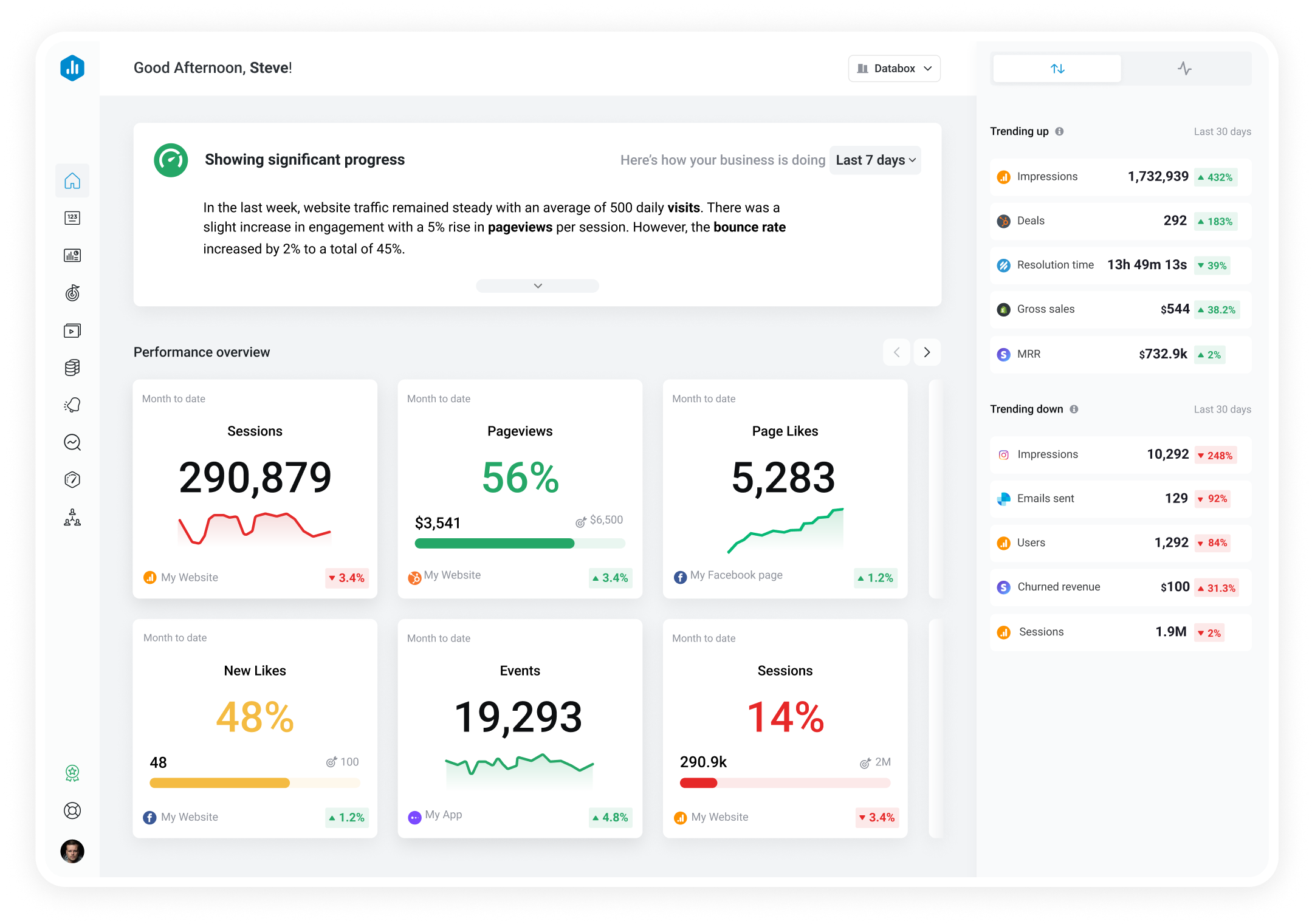
 QuickBooks
Amount (Accrual) by Product
QuickBooks
Amount (Accrual) by Product The Amount by Product metric refers to the total amount of revenue generated by each product sold in your business. It helps you identify your best-performing products and make data-driven decisions to optimize your sales strategy.
With Databox you can track all your metrics from various data sources in one place.
Used to show comparisons between values.
Databox is a business analytics software that allows you to track and visualize your most important metrics from any data source in one centralized platform.
To track Amount (Accrual) by Product using Databox, follow these steps:
 Goals
Goals Scorecards
Scorecards Metric Digest
Metric Digest Metric Builder
Metric Builder Data Calculations
Data Calculations Performance Screen
Performance Screen